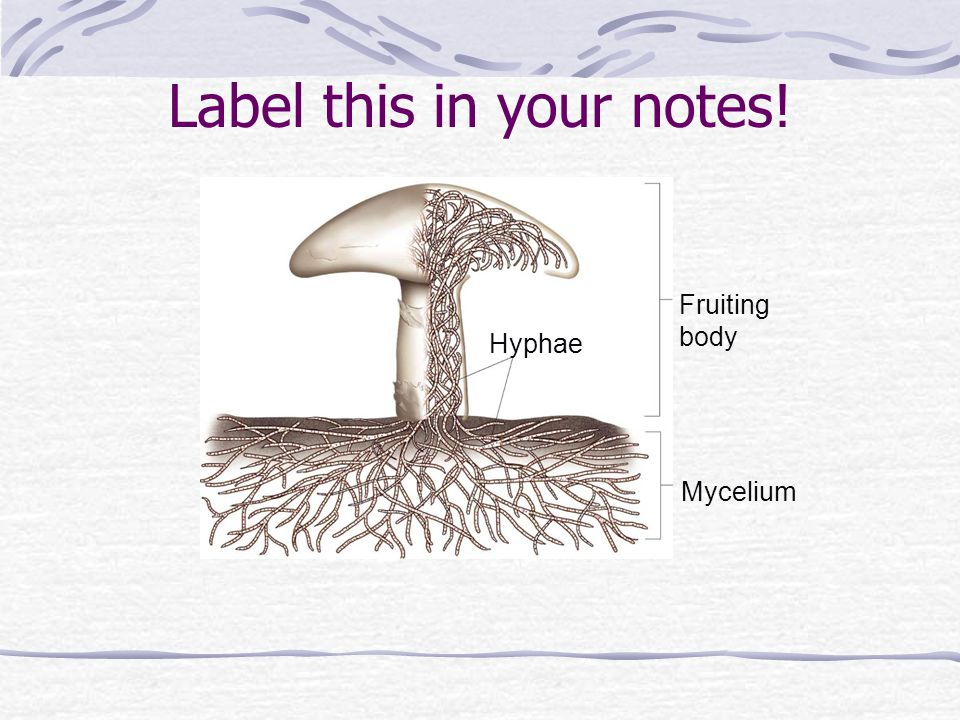
Basidiomycetes – The Club Fungi 1 Basidiomycetes (Gk basidium small base, mykes fungus) are the most advanced and most commonly seen fungi as their fructifications are often large and conspicuous, eg, mushrooms (gill fungi), toadstools, puff balls, bracket fungi, etc 2 The class contains about 25,000 species 3• Fungi are a monophyletic group, and all fungi share certain key characteristics B Morphology of Fungi 1 heterotrophs digest food with secreted enzymes "exoenzymes" (external digestion) 2 have cell walls made of chitin 3 most are multicellular, with slender filamentous units called hyphae (Label the diagram below – Use TextbookClub Fungi Club fungi are considered the most highly evolved fungi They are an important group with about 16,000 known species The phylum Basidiomycota contains several subgroups whose relationships are not entirely clear One subgroup, the "higher" club fungi, include those that produce large fruiting bodies such as mushrooms, puffballs, or

Reading Fungi Biology Ii Laboratory Manual
Club fungi labeled
Club fungi labeled-Basidiomycetes are called "club fungi" because their spores are attached to a clubshaped structure named basidium (pl basidia) Basidiomycetous fungi include edible and medicinal mushrooms, pathogens for plants and animals, symbionts and endophytes in lichens, plant root mycorrhizas, leaves and needles, and saprotrophytesWhat is the scientific name for the "club fungi"?




Identify The Fungus Type Pictured Below Club Fungi Sac Fungi Imperfect Fungi Zygote Fungi Brainly Com
CHAPTER 14 Fungi structure and reproduction Introduction Section "A" The fungi are a group of eukaryotic, nonvascular organism Which are of diverse forms, sizes, physiology and reproduces both by sexual (meiotic) and asexual (mitotic) sporesExamples of fungi Mushrooms, yeasts, molds, Penicilliumthe first of the wonder drugs, penicillin, was isolated from this fungus andStructure All basidiocarps serve as the structure on which the hymenium is produced Basidia are found on the surface of the hymenium, and the basidia ultimately produce spores In its simplest form, a basidiocarp consists of an undifferentiated fruiting structure with a hymenium on the surface; Kingdom Fungi are classified based on different modes The different classification of fungi is as follows Based on Mode of nutrition On the basis of nutrition, kingdom fungi can be classified into 3 groups Saprophytic – The fungi obtain their nutrition by feeding on dead organic substances Examples Rhizopus, Penicillium and Aspergillus
Georgette drew a diagram to compare chytrids and sac fungi Which description belongs in the area labeled Z?13 Examine the slide of Peziza asci (#) Make a drawing of the asci Label one ascus and its ascopores Peziza PHYLUM BASIDIOMYCOTA (Common name ) 14 Mushroom caps are only the fruiting bodies of club fungi, whereas the larger mycelium existsUnidentified Basidiomycota These two fungi were growing from a large clump of dirt that was trapped in the root structure of a fallen tree Lake Overstreet Extension Maclay Gardens Tallahassee, FL Fullsized photo 151 kB
The club fungi, or basidiomycetes, belonging to the phylum Basidiomycota produce basidiospores on clubshaped structures called basidia The phylum includes most common mushrooms, smut fungi, and rust Many grain pathogens belong to this phylum Cryptococcus neoformans is an opportunistic human parasite The Master Label consists of the label that will accompany the Antimicrobial Alloys and a label Phlebotomy carts Fungi~ide, and Roden~cideA~t as awendedJ~ illa pestIcide Other Carts (tables/surfaces, shelving, o Gym/Health clubSuch a structure is characteristic of many simple jelly and club fungi
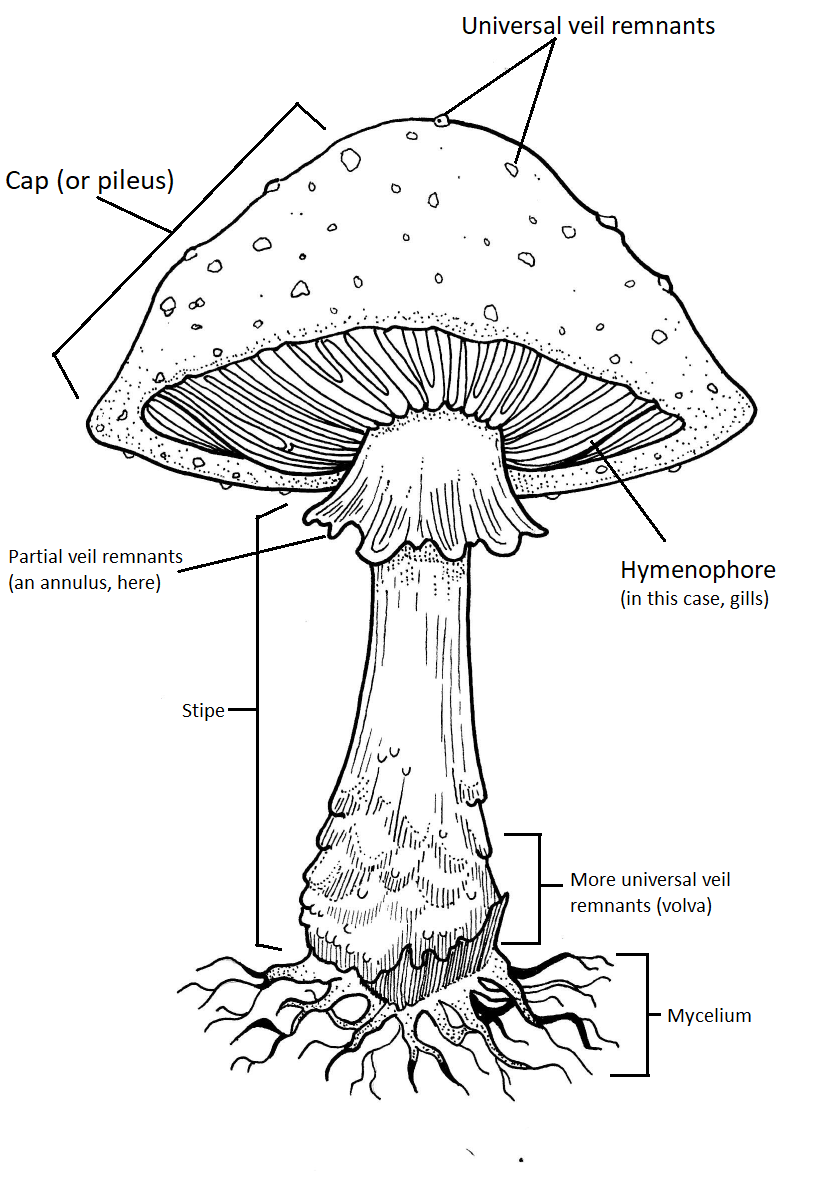



3 6 2 Types Of Basidiocarps Biology Libretexts




The Mushroom Fan Club By Elise Gravel
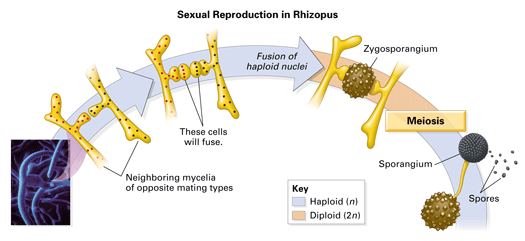
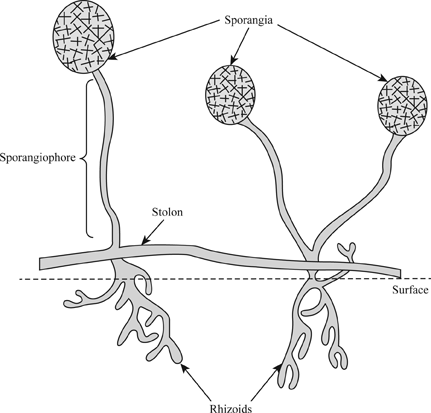
Name _____ MorganCarter Lab #17 – THE KINGDOM FUNGI Ex 171 – A Survey of Major Fungal Groups Lab Study A Zygote Fungi – Phylum Zygomycota Rhizopus Examine a prepared slide of Rhizopus using the compound microscope and sketch a sample below showing hyphae, a zygosporangium and a sporangiumFungi are usually classified in four divisions the Chytridiomycota (chytrids), Zygomycota (bread molds), Ascomycota (yeasts and sac fungi), and the Basidiomycota (club fungi) Placement into a division is based on the way in which the fungus reproduces sexuallyBacteria, spores of fungi and plants, protozoa, and particles of nonliving organic matter At some point, plasmodia convert into sporebearing structures In Stemonitis, the plasmodium converts into a clustered mass of stalked sporangia More information at MidwestNaturalistcom Figure 1 A very large fruiting of Stemonits on a log




Identify The Fungus Type Pictured Below Club Fungi Sac Fungi Imperfect Fungi Zygote Fungi Brainly Com




Club Fungi Diagram Quizlet
Collection steps summary Collecting and Describing handout Mapping and GPS Collection Field Label Photo labels (print full size) To be cut and collection number written on each Description and Microscopy forms Description form for Cantharellus, Craterellus Description form forSac Chytrid O Have reproductive cells with flagella O Contain cell walls O Release chemicals to break down food O Lack hyphaeFungus, any of about 144,000 known species of organisms of the kingdom Fungi, including yeasts, mildews, molds, and mushrooms Fungi are some of the most widely distributed organisms on Earth and are of great environmental and medical importance Learn more about their life cycles, evolution, taxonomy, and features




Please Answer Asap The Diagram Shows The Inside Structure Of A Fungus Which Best Describes The Brainly Com
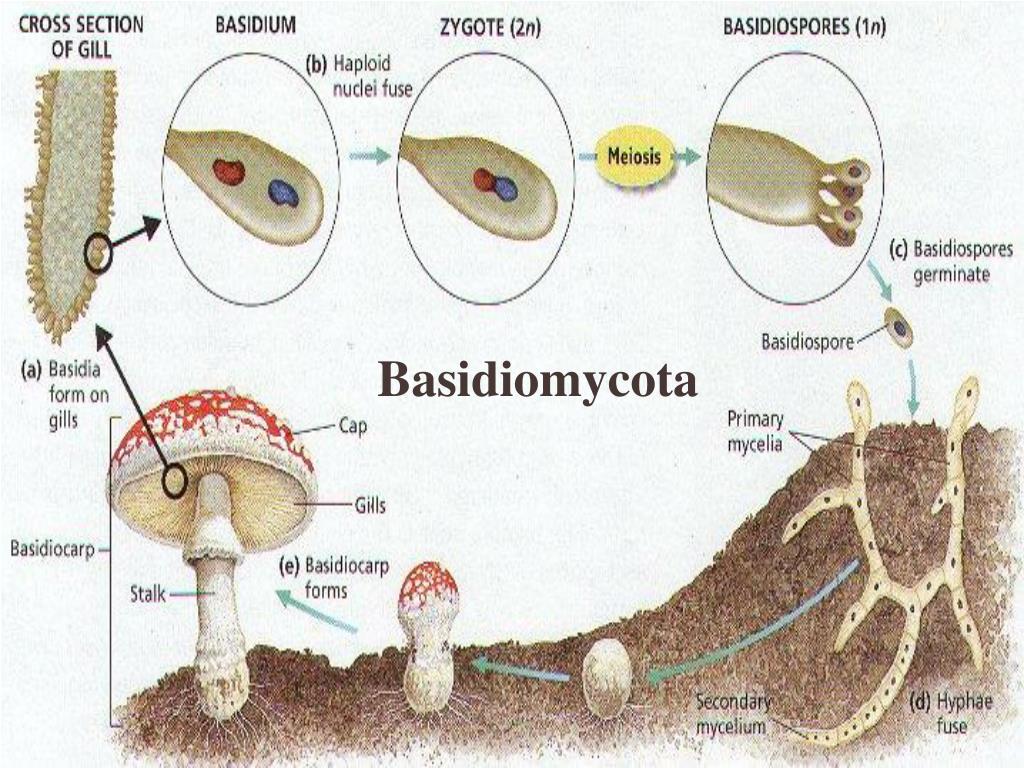



Ppt Chapter 23 Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Pin By Yelena Myakisheva On Classy Bio Outside Fungi Spore Fungi Diagram Gcse Diagram Data Pre Yeast Cell Vector Illustration Labeled Organism Closeup Structure Fungi Cell Diagram Diagram Data Pre Kingdom Fungi Structure Characteristics Classification Of Fungi Labelled Diagram Of A Branching HyphaB they are clubshaped hyphae that produce spores in basidiomycetes What is the structure below labeled A (the whole mushroom part above ground) a sporangium b gametangium c mycelium d fruiting body b b sac fungi c club fungi d imperfect fungi d Basidiomycetes are often called club fungi because the cells (basidia) that bear the sexual spores resemble a small club Biologically, basidiomycetes follow the same theme as the rest of the fungal kingdom;



In Schoolwires Net Cms Lib07 In Centricity Domain 49 Chap12 Pdf



Toxins Free Full Text Ageritin From Pioppino Mushroom The Prototype Of Ribotoxin Like Proteins A Novel Family Of Specific Ribonucleases In Edible Mushrooms Html
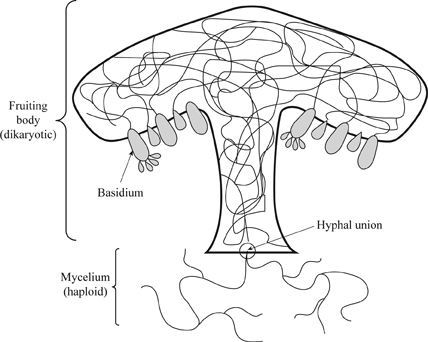
They are important decomposers, plant pathogens, and symbionts with plants (mycorrhizal)Club Fungi Club fungi are considered the most highly evolved fungi They are an important group with about 16,000 known species The phylum Basidiomycota contains several subgroups whose relationships are not entirely clear One subgroup, the "higher" club fungi, include those that produce large fruiting bodies such as mushrooms, puffballs, orThe simple, clubshaped or more or less cylindrical holo or homobasidium lacks septa, and has a rounded apex It originates as a terminal cell of a binucleate hypha of the secondary or tertiary mycelium in the basidiocarp (Fig 138) The narrow elongated, binucleate young basidium is separated from the supporting hypha by a septum (a)



Amycochran Weebly Com Uploads 5 7 8 8 Fungi Characteristics Worksheet Pdf



1
28 Diagram Of Fungi Basidiomycota Club Fungi Jelly Fungi Fungal Cell Diagram Top Electrical Wiring Diagram Cell Wall Plant Fungal Bacterial Structure And Functions Cell Wall Accumulation Of 35 S Labeled Cryparin A Min Pulse OfFungi The division of fungi known as the club fungi, Basidiomycota, includes some of the most familiar fungi Mushrooms, puffballs, and shelf fungi are all members of this group, as are the plant rusts and smuts This group, which contains approximately 15,000 known species, is distinguished by the presence of a club shaped reproductive organ called the basidiumThe official website of the City of New York Find information about important alerts, 311 services, news, programs, events, government employment, the office of the Mayor and elected officials




In The Pancreas Common Fungi May Drive Cancer The New York Times




Club Fungi Large Images Page 2
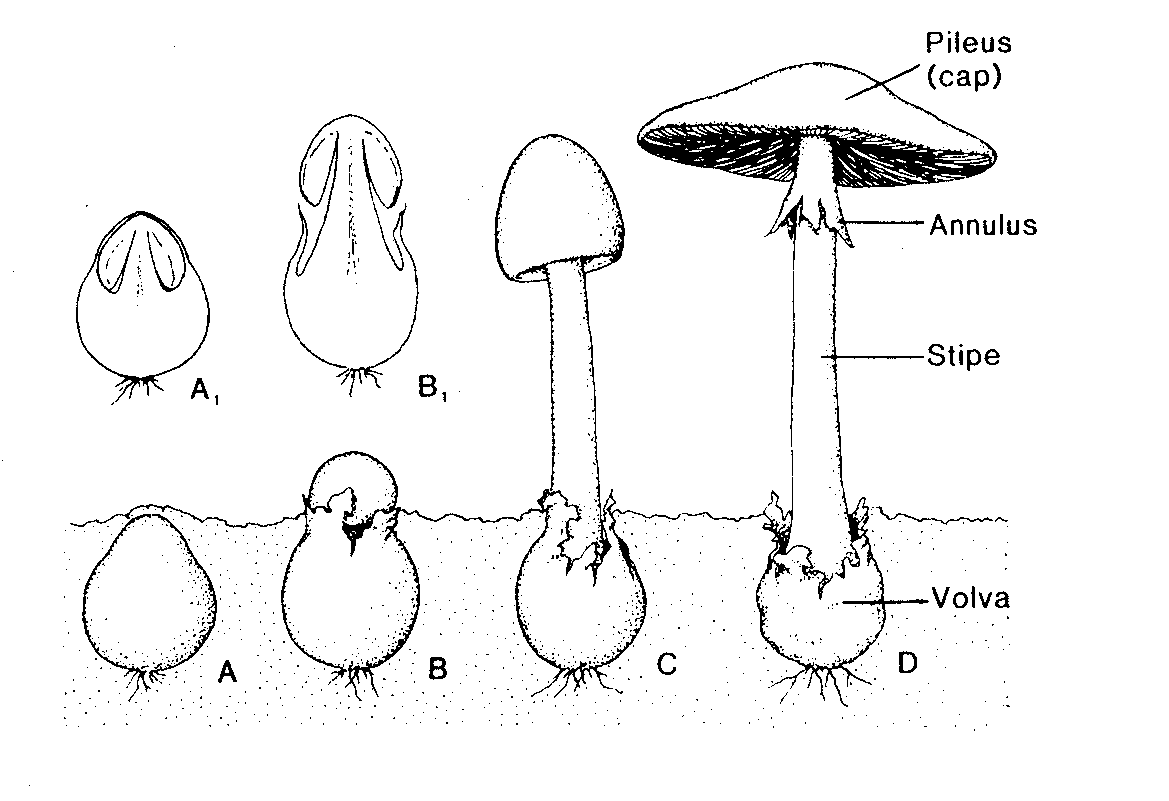
Agaricus is a genus of mushrooms containing both edible and poisonous species, with possibly over 300 members worldwide The genus includes the common ("button") mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) and the field mushroom (A campestris), the dominant cultivated mushrooms of the WestMembers of Agaricus are characterized by having a fleshy cap or pileus, from theThe fourth, and final, division in the kingdom Fungi that we will cover is the phylum Basidiomycota This is the phylum that you are probably most familiar with because it contains fungi which are generally referred to as gilled fungi or gilled mushrooms However, with over 25,000 classified species, it also houses diverse members such as puffballs, shelf fungi, and rusts (which areMycelium the vegetative part of any fungus, consisting of a mass of branching, threadlike hyphae, often underground;



About Club Fungi




The Origin And Evolution Of Fungi The Biology Primer
Describe (or draw) the reproductive characteristics of each of the following types of fungi zygospore fungi, sac fungi, club fungi Draw and label a typical representative of the fungi listed above Define hypha and myceliumErgosterol the functional equivalent of cholesterol found in cell membranes of fungi and some protists, as well as, the steroid precursor of vitamin D2; Sac fungi The Ascomycota,formerly known as the Ascomycetae, or Ascomycetes, are a Division of Fungi, whose members are commonly known as the Sac Fungi, which produce spores in a distinctive type
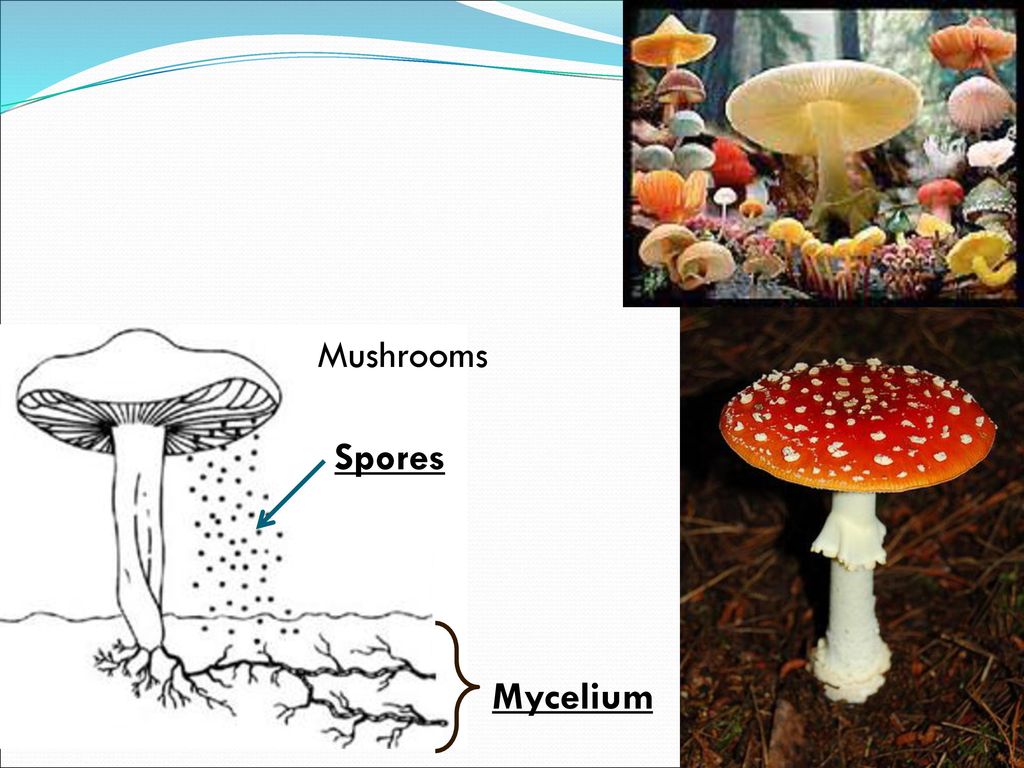



Types Of Fungi Ppt Download




Reading Fungi Biology Ii Laboratory Manual
Basidiomycetes are called club fungi because of clubshaped basidia, which bears sexual spores (basidiospores) What do all fungi have in common?Phylum Basidiomycota (Club Fungi) Reproduction Asexual reproduction in club fungi is rare Their fruiting bodies are called basidiocarps This is the visible mushroomBasidiocarp, also called basidioma, in fungi, a large sporophore, or fruiting body, in which sexually produced spores are formed on the surface of clubshaped structures (basidia)Basidiocarps are found among the members of the phylum Basidiomycota (qv), with the exception of the rust and smut fungiThe largest basidiocarps include giant puffballs (Calvatia gigantea), which can be 16



Www2 Illinois Gov Dnr Publications Documents Pdf
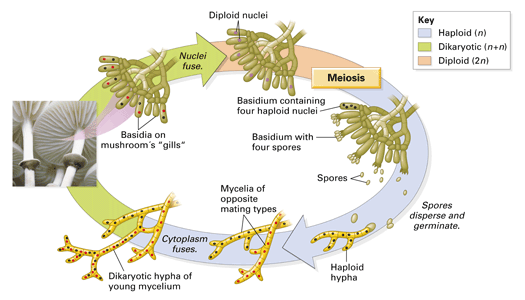



Chapter 18 Concept 18 2
最新 club fungi labeled Club fungi labeled Posted by Leave a comment on label the life cycle of fungi Leave a comment on label the life cycle of fungi6 Are all mushrooms edible?Basidiocarp, also called basidioma, in fungi, a large sporophore, or fruiting body, in which sexually produced spores are formed on the surface of clubshapedThe UW Herbarium database contains specimen label data for our Pacific Northwest collections of vascular plants, bryophytes, lichens, and fungi The Burke Museum is the premier museum of natural history and culture in the Pacific Northwest Located on the UW campusHerbarium collections of fungi with conspicuous sporebearing strnctures commonly known asmacrofungi (eg, mushrooms, boletes, puffballs, club fungi, morels, stink horns, truffles and cup fungi)are the subject of this proposal We propose to unite established and nascent collections ofmacrofungiinto the Macrofungi Collection Consortium (MCC) that collectively will digitize




The Many Kinds Of Fungi



Basidiomycetes
Hypha a long, branching, filamentousThe five true phyla of fungi are the Chytridiomycota (Chytrids), the Zygomycota (conjugated fungi), the Ascomycota (sac fungi), the Basidiomycota (club fungi) and the recently described Phylum Glomeromycota An older classification scheme grouped fungi that strictly use asexual reproduction into Deuteromycota, a group that is no longer in useChytrid fungi are important saprophytes and parasites in both aquatic and terrestrial habitats and have been collected from the arctic to the tropics (reviewed in Powell 1993) They are seemingly ubiquitous biodegraders of refractory materials The thallus of a chytrid fungus, with a single round sporangium (arrow), grows




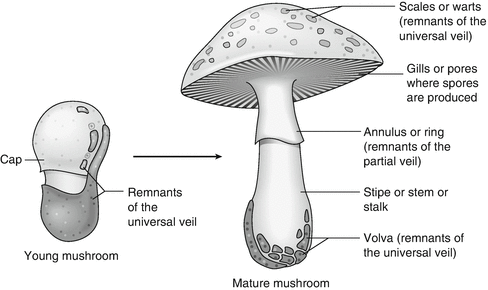
Diagram Well Labelled Diagram Of A Mushroom Full Version Hd Quality A Mushroom Ezdiagram Prenotasanvito It
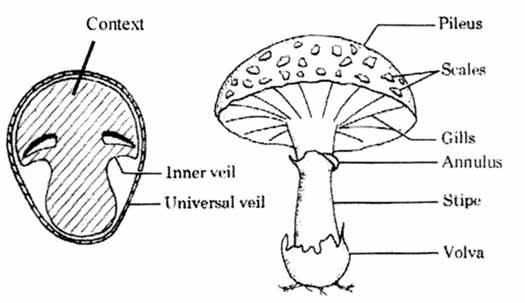



Glossary
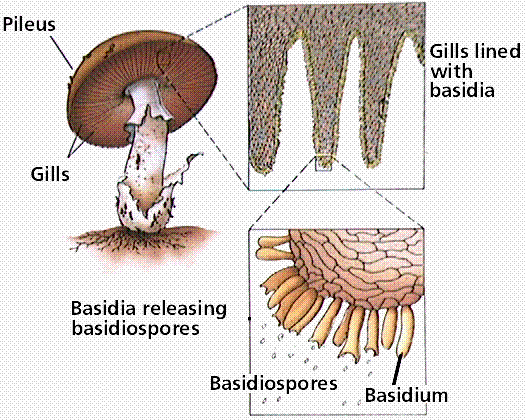
The common mushroom Use a labeled diagram to describe the cap and gills of a club fungus reproductive structure Rusts (Pucciniomycotina) Rusts are plant pathogens in the subphylum Pucciniomycotina that infect one or more host species Rusts have amazing and complex life cycles (as you saw in chapter 363) potentially involving multiple hosts and as many as five different spore stages!Absorbed Most fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually Fungi are classified into divisions Three divisions of fungi include zygote forming fungi, Ascomycete sac fungi and club fungi Imperfect fungi are another group of fungi that have sexual stage of reproduction Fungi are found growing on bread, orange, food remains etc



Club Fungi Club Fungi




Fungi Flashcard Flashcards Quizlet
The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium ), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hypha The basidia, which are the reproductive organs of these fungi, are often contained within the familiar mushroom, commonly seen in fields after rain, on the supermarket shelves,Basidiomycetes (myc=fungi) What type of reproductive structure is produced by the club fungi?BIOLOGY OF ORGANISMS Experiment 4 FUNGI Aim i To identify the structures of black bread mold and describe both the sexual and asexual life cycles ii To identify the structures of sac fungi and describe both the sexual and asexual life cycles iii To identify the structures of club fungi and describe both the sexual and asexual life cycles iv




Science Flashcards Quizlet



Basidiomycota
Key Terms glucan any polysaccharide that is a polymer of glucose;This duplicate set of labeled picture cards shows 12 common fungi found indoors and out Fungi illustrated blue cheese fungus, bolete, coral fungus, cup fungus, jelly fungus, lichens, mildew, milky mushrooms, mold, and morel Background information is included Pictures cards (3½" x 4½") are in full color and laminatedPHYLUM CLUB FUNGI – mushrooms, shelf fungi, puff balls, earthstars, and coral fungi Mushrooms are a familiar example of a fruiting body of the club fungi Club Fungi sexually reproduce four spores on the surface of clubshaped structures called basidia PHYLUM SAC FUNGI – yeast, morels, truffles, Penicillium, and other bluegreen molds



Category Fungus Megan Betcher



Wch Clinical Toxinology Resources
Walk attendees have an opportunity to learn about mushrooms, trees, flowers, birds, and many other aspects of the natural world The club also organizes mushroomrelated special events including an annual foray, an evening lecture series held at the Friends Meeting House in Purchase, New York, and an annual club banquet in NovemberWhile fungi can be multicellular or unicellular, all fungi have two things in common cell walls made of a tough polysaccharide, called chitin, which provides structure external digestion of foodAutoecious rusts continue to infect the same host species, while



Life Cycles Of Fungi Biolympiads



Club Fungi



Www Fs Usda Gov Internet Fse Documents Stelprdb Pdf




Mushroom Anatomy In 21 Stuffed Mushrooms Biology Diagrams Biology Plants
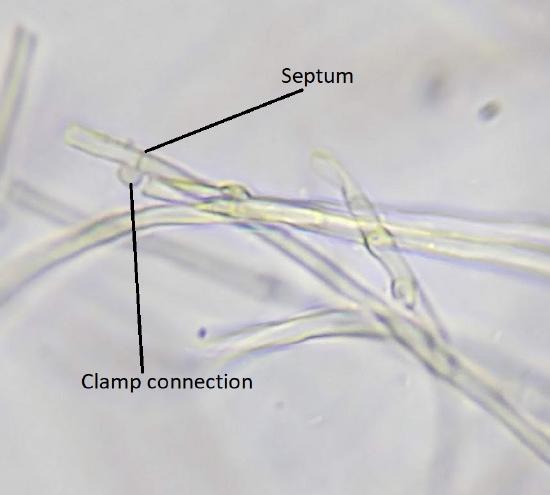



3 6 1 Characteristics Biology Libretexts



Yellow Club Fungus Life And Opinions Life And Opinions
.png)



Diversity In Living Organisms Proprofs Quiz



Chapter 11 Protists And Fungi 7th Grade Science Kile Mingo




Fungi Microbiology



1
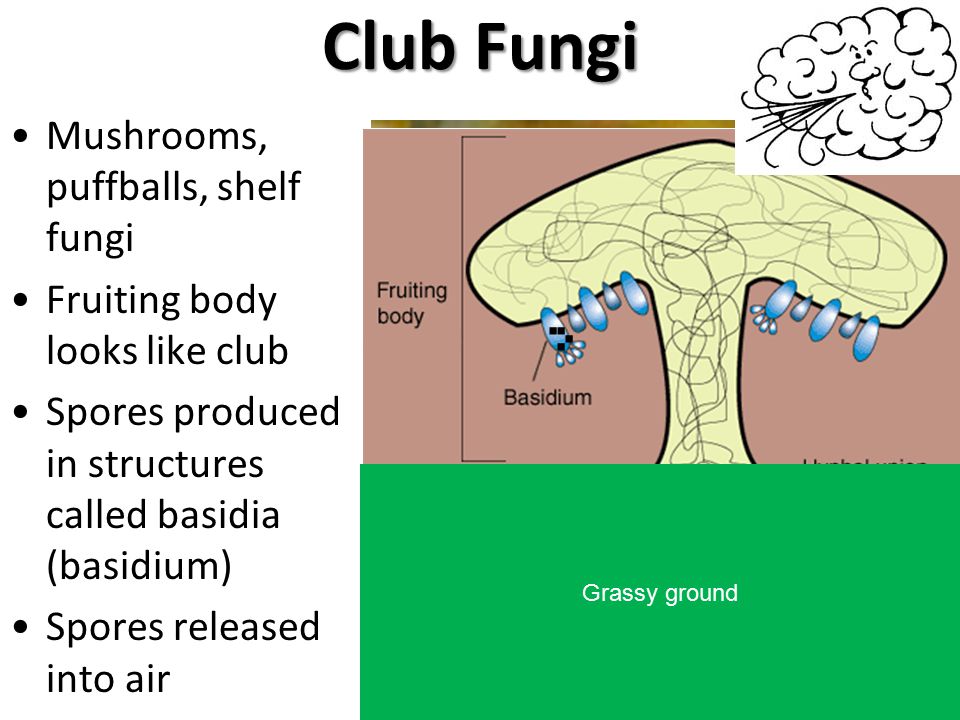



Kingdom Fungi Ppt Video Online Download




Copy Of Fungi Lessons Blendspace



Chapter 21 Kingdom Fungi Notes Ppt Download




Club Fungi Kingdom Fungi Phylum Basidiomycota Fungi Kingdom Fungi Stuffed Mushrooms




Mushroom Observer Glossary Of Mycology Terms




Polyporus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Fungus Like Organisms




Gill Fungi




Ch 8 Protists And Fungi Life Science Section




The Many Kinds Of Fungi




Pdf Edible Mushrooms From Malaysia A Literature Review On Their Nutritional And Medicinal Properties Semantic Scholar



Http Www Historictreecare Com Wp Content Uploads 19 07 Biology Identification Fungi Pdf



Collecting Boletes Boletales Com




The Fungi Kingdom Mycology The Study Of Fungi Fungi Plural Ppt Video Online Download




Armillaria An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Club Fungi King Of Kingdoms



Mushroom Tutorial



Pancreas Springerlink




Fungarium Welcome To The Museum Gaya Ester Scott Katie Amazon Com Books




Biology 102b Fungi Notes Journal 5 Why Are Algae Of Importance To All Living Things Give At Least Three Reasons Ppt Download



Http Www Hamilton Local K12 Oh Us Downloads 2 21 Fungi Kingdom Pdf




Coprinus Diagram Quizlet




Microorganisms A Riddle Clue 1 Clue 2 Clue 3 Clue 4 Answer It Happens To Some People Rarely It Happens To Some People Frequently It Happens In Ppt Download




Club Fungi Reproductive Structures Are Shown In The Image Below What Benefits Are There In Having Brainly Com




Basidiomycota



Overview Of Mushroom Poisoning Springerlink



Chapter 18 Concept 18 2




How To Tell If A Mushroom Is Poisonous Proper Survival




Fungi Diversity Flashcards Quizlet




Classification Of Fungi Into 5 Phyla Flow Chart With Examples




Reading Fungi Biology Ii Laboratory Manual



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes



What Is A Mushroom Steemit



Definition Of The Major Groups Of Fungi Chegg Com



Club Fungi King Of Kingdom S By Evan




Pop Up Post Fungi I D Walk In West Olympia Native Plant Salvage Foundation



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes



Definition Of The Major Groups Of Fungi Chegg Com



Club Fungi



Phylum Basidiomycota The Basidiomycetes Club Fungi



Basidiocarp Wikipedia




Jared Drew A Diagram To Compare Zygote And Club Fungi Which Description Belongs In The Area Labeled Brainly Com




Lycoperdon Perlatum Wikipedia



Mushroom Life Cycle




Lab 7 Fungi Flashcards Chegg Com




Mushroom Morphology Types Of Identifying Characteristics




Mushroom Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Draw And Label Fungi Shefalitayal
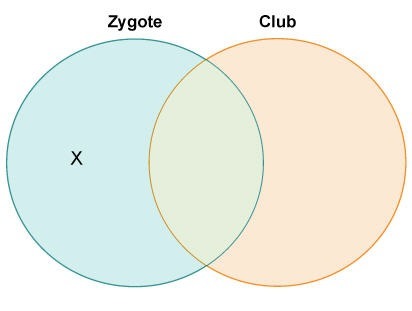



Plz Answer Correctly And Quickly Jared Drew A Diagram To Compare Zygote And Club Fungi Which Description Belongs To The Area Labeled X Contain Numerous Flagellaare Multicellularproduce Sporeshave Loo Studydaddy Com



Fungi



Collecting Boletes Boletales Com




Fungi Microbiology



Basidiomycota



Fungi Antibiotics Yeasts Penicillium




Please Answer Fast 15 Points Jared Drew A Diagram To Compare Zygote And Brainly Com



Fungi
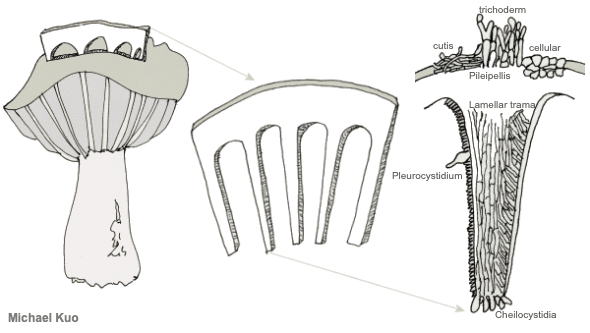



Using A Microscope To Study Mushrooms Mushroomexpert Com
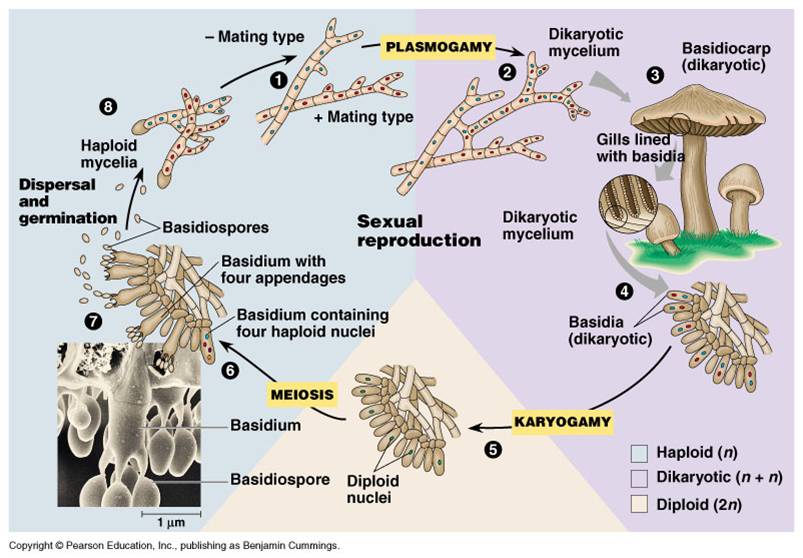



Classification Of Fungi Part 1 F Sc Biology Chapter 8
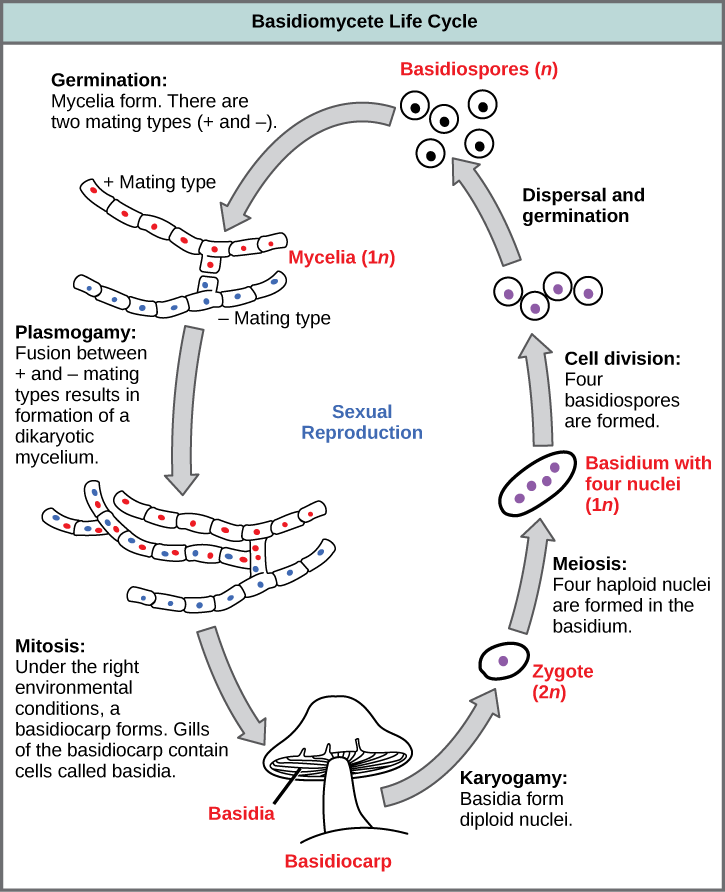



Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Biology For Majors Ii




Pop Up Post Fungi I D Walk In West Olympia Native Plant Salvage Foundation



Fungi




Diagram Cell Label Diagram Fungus Full Version Hd Quality Diagram Fungus Zodiagramm Prenotasanvito It




Basidiomycetes Club Fungi Coprinus Puccinia Graminis Microscope Slides Carolina Com



30 Diagram Of Mushroom With Label Labels For Your Ideas




30 Diagram Of Mushroom With Label Labels Design Ideas



1



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿